
CKA, CKAD Prep
In the summer of 2022, I decided that it was time to try again to learn a bit about Kubernetes because it’s something that becomes more and more …

What does Edge AI really mean? I was asked this question several times over and decided to share my thoughts on this topic. Edge AI commonly refers to components required to run an AI algorithm locally on a device, it’s also referred to as on-Device AI. Of late it means running Deep learning algorithms on a device and most articles tend to focus only on one component i.e. inference. This article will shed some light on other pieces of this puzzle.
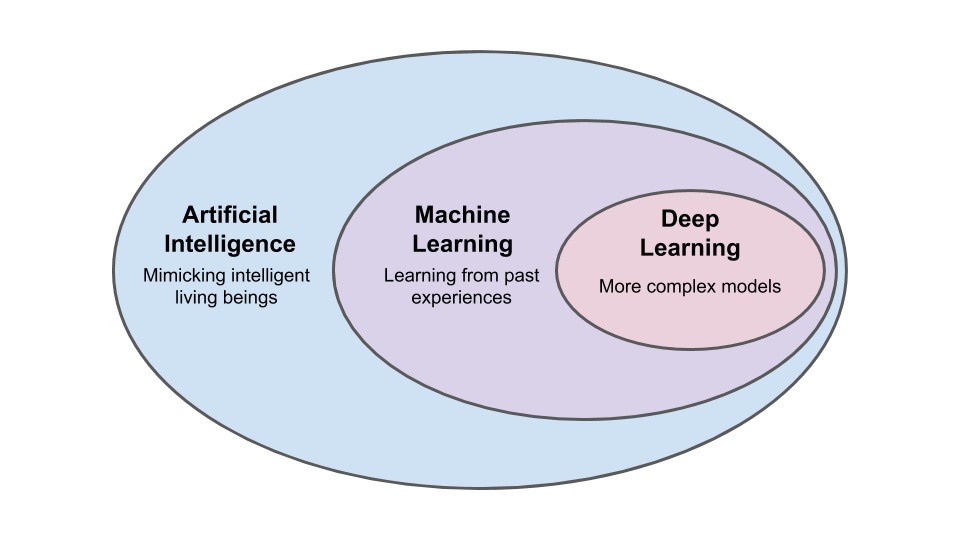
All deep learning algorithms can be considered part of machine learning and artificial intelligence, but not all AI algorithms are machine learning (or deep learning).
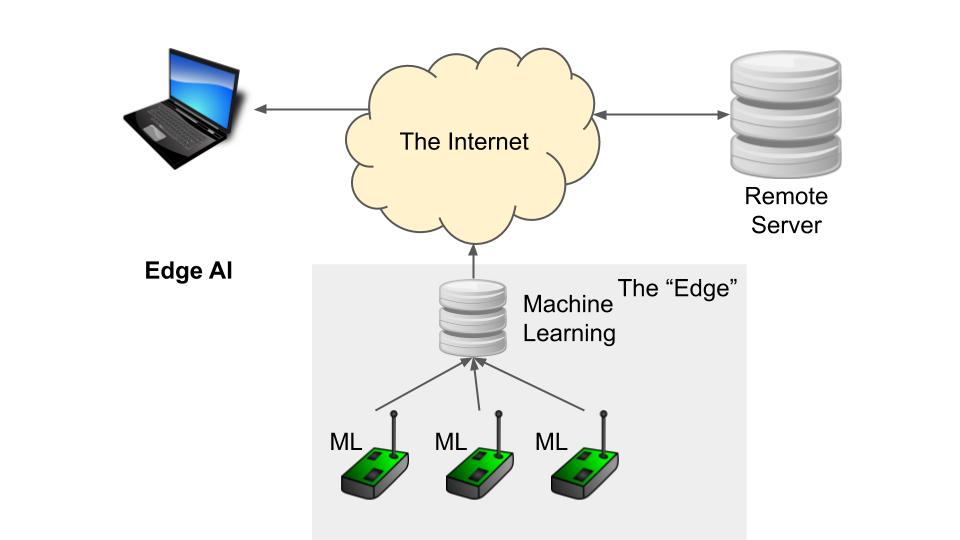
Most IoT configurations look something like the image above. Sensors or devices are connected directly to the Internet through a router, providing raw data to a backend server. Machine learning algorithms can be run on these servers to help predict a variety of cases that might interest managers.
However, things get tricky when too many devices begin to clog the network traffic. Perhaps there’s too much traffic on local WiFi or there’s too much data being piped to the remote server (and you don’t want to pay for that). To help alleviate some of these issues, we can begin to run less complex machine learning algorithms on a local server or even the devices themselves.
This is known as “Edge AI.” We’re running machine learning algorithms on locally owned computers or embedded systems as opposed to on remote servers. While the algorithms might not be as powerful, we can potentially curate the data before sending it off to a remote location for further analysis.
NVIDIA® Jetson™ systems provide the performance and efficiency to run autonomous machine software, faster and with less power. Each is a complete System-on-Module (SOM) combining CPU, GPU, PMIC, DRAM, and Flash storage – and using a single shared software development environment, saving you time and money.
Jetson AGX Xavier is the first computer designed specifically for autonomous machines. It has six engines onboard for accelerated sensors data processing and running autonomous machines software, offerings the performance and power efficiency for fully autonomous machines.

Jetson AGX Xavier 8GB is a lower-power lower-price Jetson AGX Xavier offering full hardware and software compatibility with the existing Jetson AGX Xavier. It consumes a maximum of 20W for the full module while delivering up to 20 TOPS of AI performance.
NVIDIA® Jetson Nano™ Developer Kit is a small, powerful computer that lets you run multiple neural networks in parallel for applications like image classification, object detection, segmentation, and speech processing. All in an easy-to-use platform that runs in as little as 5 watts.

Jetson Nano module is a small AI computer that has the performance and power efficiency needed to run modern AI workloads, including multiple neural networks in parallel and process data from several high-resolution sensors simultaneously. This makes it the perfect entry-level option to add advanced AI to embedded products.
However, things get tricky when too many devices begin to clog the network traffic. Perhaps there’s too much traffic on local WiFi or there’s too much data being piped to the remote server (and you don’t want to pay for that). To help alleviate some of these issues, we can begin to run less complex machine learning algorithms on a local server or even the devices themselves.
Interest in edge computing continues to build, as does confusion surrounding the architecture. The situation is similar when it comes to artificial intelligence. The prospect of moving AI to the edge might sound like a recipe for even more confusion.
Still, the concept of edge AI is increasingly hard for industrial and enterprise organizations to ignore. Resource-intensive operations such as deep learning and computer vision have traditionally taken place in centralized computing environments. But the growing availability of high-performance networking and computing hardware opens up the possibility to shift that activity from a centralized cloud architecture to the edge.
Located outside of traditional data centers and the cloud, the edge is concentrated at the “last mile” of the network and it is as close as possible to the things and people producing data or information. With edge AI, telecommunications companies can develop next-generation services to offer their customers, providing new revenue streams.

In the summer of 2022, I decided that it was time to try again to learn a bit about Kubernetes because it’s something that becomes more and more …

Recently, I found a very interesting open-source project called mosdns, which is regarded as the next-generation DNS resolver from the user’s …